Springboot源码解析
1. 依赖
1.1 依赖管理
spring-boot-starter-parent
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
将spring-boot-starter-parent依赖作为Spring Boot项目的统一父项目依赖管理,并将项目版本号统一为2.2.2.RELEASE,该版本号根据实际开发需求是可以修改的
spring-boot-starter-parent中定义了一些基本配置信息,比如配置文件的加载:
<includes>
<include>**/application*.yml</include>
<include>**/application*.yaml</include>
<include>**/application*.properties</include>
</includes>
在加载配置文件时,会先加载yml文件,然后是yaml文件,最后加载properties文件,如果文件中有相同参数的配置,properties中的会覆盖其他配置文件中的内容
parent中的: spring-boot-dependencies
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath>../../spring-boot-dependencies</relativePath>
</parent>
dependencies中的定义了所有依赖的版本号,通过管理依赖的版本
<properties>
<activemq.version>5.15.11</activemq.version>
<antlr2.version>2.7.7</antlr2.version>
<appengine-sdk.version>1.9.77</appengine-sdk.version>
......
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-test</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
.........
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
1.2 依赖传递
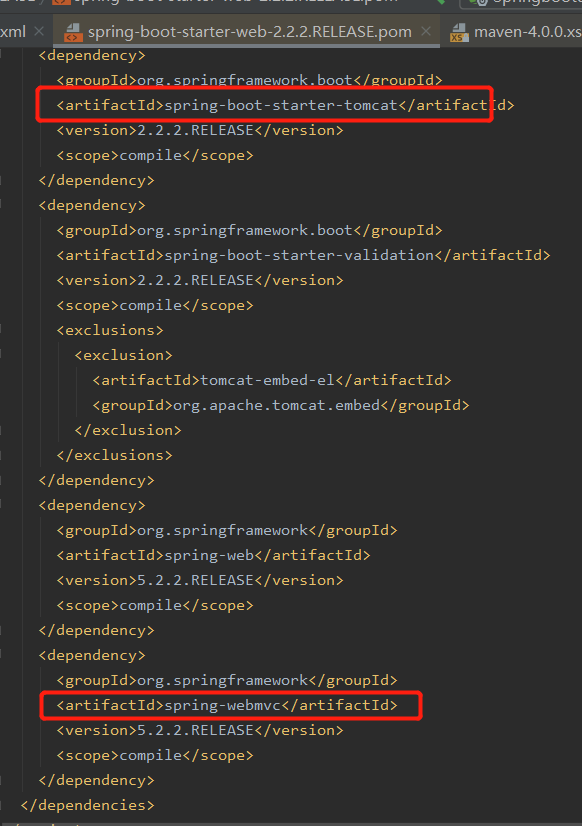
spring-boot-starter-web
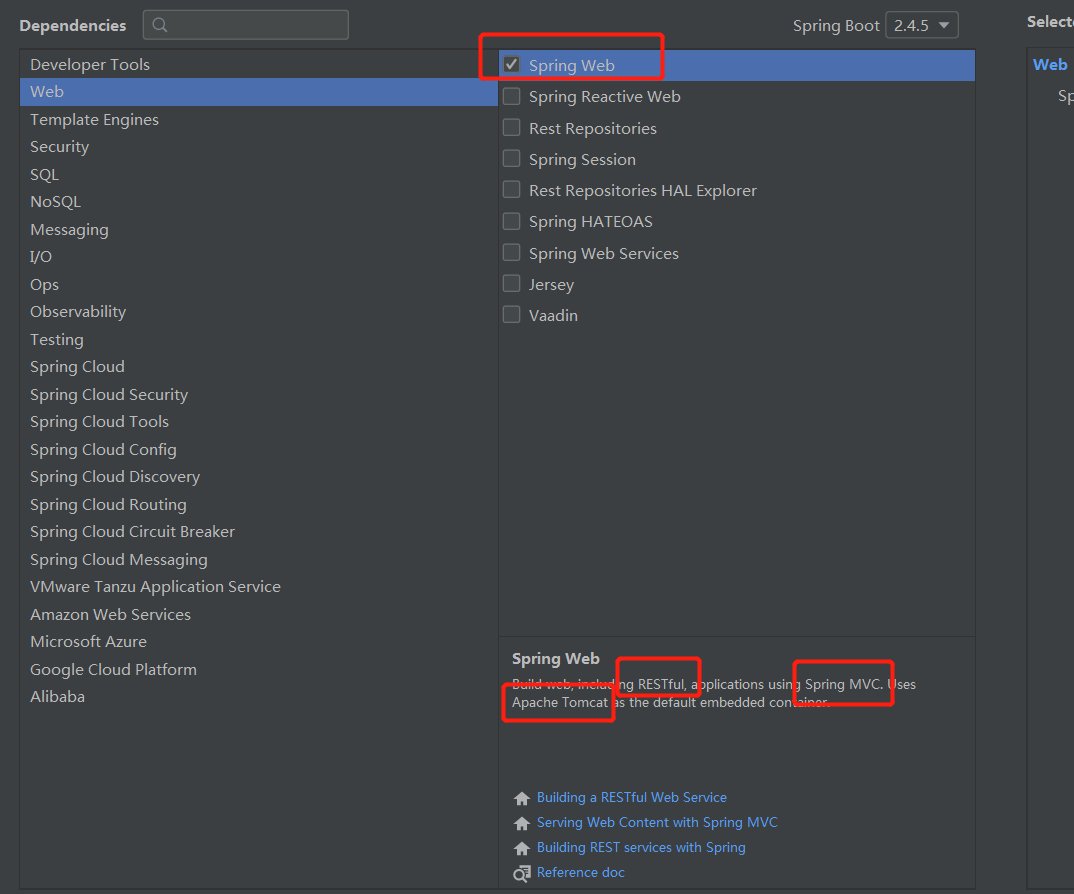 在使用https://start.spring.io 创建项目时,勾选springweb,会有如下提示:
在使用https://start.spring.io 创建项目时,勾选springweb,会有如下提示:
构建web,包括RESTful,应用程序使用Spring MVC。使用Apache Tomcat作为默认的嵌入式容器
springweb的依赖中包含Tomcat和springMVC的依赖,所以引入springweb后不需要再引入Tomcat和springMVC的依赖
2. @SpringBootApplication注解
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootdemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootdemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
/**
* Indicates a {@link Configuration configuration} class that declares one or more
* {@link Bean @Bean} methods and also triggers {@link EnableAutoConfiguration
* auto-configuration} and {@link ComponentScan component scanning}. This is a convenience
* annotation that is equivalent to declaring {@code @Configuration},
* {@code @EnableAutoConfiguration} and {@code @ComponentScan}.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @since 1.2.0
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) //注解的适用范围,Type表示注解可以描述在类、接口、注解或枚举中
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) ///表示注解的生命周期,Runtime运行时
@Documented ////表示注解可以记录在javadoc中
@Inherited //表示可以被子类继承该注解
@SpringBootConfiguration //// 标明该类为配置类
@EnableAutoConfiguration // 启动自动配置功能
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { // 包扫描器 <context:component-scan base-package="com.xxx.xxx"/>
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
//省略中间内容
}
SpringBootApplication中主要看下边三个注解:
- @SpringBootConfiguration // 标明该类为配置类
- @EnableAutoConfiguration // 启动自动配置功能
- @ComponentScan // 包扫描器
2.1 @SpringBootConfiguration
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration //配置类
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {
}
SpringBootConfiguration有一个核心注解@Configuration,该注解是Spring框架提供的,表示当前类为一个配置类(XML配置文件的注解表现形式),并可以被组件扫描器扫描,由此可见,@SpringBootConfiguration注解的作用与@Configuration注解相同,都是标识一个可以被组件扫描器扫描的配置类,只不过@SpringBootConfiguration是Spring Boot进行了重新封装命名
2.2 @EnableAutoConfiguration // 启动自动配置功能
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage //自动配置包 : 会把@springbootApplication注解标注的类所在包名拿到,并且对该包及其子包进行扫描,将组件添加到容器中
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) //可以帮助springboot应用将所有符合条件的@Configuration配置都加载到当前SpringBoot创建并使用的IoC容器(ApplicationContext)中
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
//省略中间内容
}
EnableAutoConfiguration中重要的是两个注解
- @AutoConfigurationPackage,会扫描当前启动类所在的包及其子包下的组件,并注册一个AutoConfigurationPackages
- @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) 该注解的作用是向容器中导入一个AutoConfigurationImportSelector组件,这个组件会加载所有满足条件的配置类并注册到容器中
2.2.1 @AutoConfigurationPackage
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
//spring框架的底层注解,它的作用就是给容器中导入某个组件类,
//例如@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class),它就是将Registrar这个组件类导入到容器中
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class) // 默认将主配置类(@SpringBootApplication)所在的包及其子包里面的所有组件扫描到Spring容器中
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
}
主要看该注解中的@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class) 向容器中导入AutoConfigurationPackages下的Registrar类,而Register中的registerBeanDefinitions会注册一个AutoConfigurationPackages
/**
* {@link ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar} to store the base package from the importing
* configuration.
*/
static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, DeterminableImports {
// 获取的是项目主程序启动类所在的目录
//metadata:注解标注的元数据信息
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// 注册一个AutoConfigurationPackages
// new PackageImport(metadata).getPackageName()返回值为当前启动类所在的包名 比如:com.example
register(registry, new PackageImport(metadata).getPackageName());
}
@Override
public Set<Object> determineImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
return Collections.singleton(new PackageImport(metadata));
}
}
public static void register(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, String... packageNames) {
// 如果已经存在该 BEAN ,则修改其包(package)属性
// BEAN 就是 AutoConfigurationPackages,用于存储自动配置包以供稍后引用
if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(BEAN)) {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = registry.getBeanDefinition(BEAN);
ConstructorArgumentValues constructorArguments = beanDefinition.getConstructorArgumentValues();
// 将构造函数的第一个参数设置为包名列表
constructorArguments.addIndexedArgumentValue(0, addBasePackages(constructorArguments, packageNames));
// 如果不存在该 BEAN ,则创建一个 Bean ,并进行注册
} else { GenericBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new GenericBeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setBeanClass(BasePackages.class);
// 将beanClass设置为BasePackages
beanDefinition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addIndexedArgumentValue(0, packageNames);
// 将构造函数的第一个参数设置为包名列表,也就是BasePackages的构造函数
beanDefinition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
// 注册beanDefinition
registry.registerBeanDefinition(BEAN, beanDefinition);
}
}
2.2.2 AutoConfigurationImportSelector 这个类会加载并注册所有满足条件的配置类
2.2.2.1 process() 因为版本不同,会调用不同的selectImports:AutoConfigurationImportSelector#selectImports() 或者AutoConfigurationGroup#selectImports()
此处从AutoConfigurationGroup下的process方法开始
@Override
public void process(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata, DeferredImportSelector deferredImportSelector) {
// 断言
Assert.state(
deferredImportSelector instanceof AutoConfigurationImportSelector,
() -> String.format("Only %s implementations are supported, got %s",
AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class.getSimpleName(),
deferredImportSelector.getClass().getName()));
// 获得 AutoConfigurationEntry 对象
// 1. getAutoConfigurationMetadata 获取AutoConfigurationMetadata
// 2. getAutoConfigurationEntry获取AutoConfigurationEntry
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = ((AutoConfigurationImportSelector) deferredImportSelector)
.getAutoConfigurationEntry(getAutoConfigurationMetadata(), annotationMetadata);
// 添加到 autoConfigurationEntries 中
this.autoConfigurationEntries.add(autoConfigurationEntry);
// 添加到 entries 中
for (String importClassName : autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations()) {
this.entries.putIfAbsent(importClassName, annotationMetadata);
}
}
1. getAutoConfigurationMetadata 获取AutoConfigurationMetadata
private AutoConfigurationMetadata getAutoConfigurationMetadata() {
if (this.autoConfigurationMetadata == null) {
// 查看autoConfigurationMetadata的初始化loadMetadata方法
this.autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
}
return this.autoConfigurationMetadata;
}
final class AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader {
protected static final String PATH = "META-INF/" + "spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties";//文件中为每个配置类的加载条件
private AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader() {
}
public static AutoConfigurationMetadata loadMetadata(ClassLoader classLoader) {
//重载方法
return loadMetadata(classLoader, PATH);
}
static AutoConfigurationMetadata loadMetadata(ClassLoader classLoader, String path) {
try {
//1.读取spring-boot-autoconfigure.jar包中spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties的信息生成urls枚举对象
// 获得 PATH 对应的 URL 们
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null) ? classLoader.getResources(path) : ClassLoader.getSystemResources(path);
// 遍历 URL 数组,读取到 properties 中
Properties properties = new Properties();
//2.解析urls枚举对象中的信息封装成properties对象并加载
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
properties.putAll(PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(new UrlResource(urls.nextElement())));
}
// 将 properties 转换成 PropertiesAutoConfigurationMetadata 对象
//根据封装好的properties对象生成AutoConfigurationMetadata对象返回
return loadMetadata(properties);
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load @ConditionalOnClass location [" + path + "]", ex);
}
}
static AutoConfigurationMetadata loadMetadata(Properties properties) {
return new PropertiesAutoConfigurationMetadata(properties);
}
}
2. getAutoConfigurationEntry获取AutoConfigurationEntry
/**
* 获得 AutoConfigurationEntry 对象
*
* Return the {@link AutoConfigurationEntry} based on the {@link AnnotationMetadata}
* of the importing {@link Configuration @Configuration} class.
* @param autoConfigurationMetadata the auto-configuration metadata
* @param annotationMetadata the annotation metadata of the configuration class
* @return the auto-configurations that should be imported
*/
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata, AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
// 1. 判断是否开启注解。如未开启,返回空串
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
// 2. 获得注解的属性
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
// 3. getCandidateConfigurations()用来获取默认支持的自动配置类名列表
// spring Boot在启动的时候,使用内部工具类SpringFactoriesLoader,查找classpath上所有jar包中的META-INF/spring.factories,
// 找出其中key为org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration的属性定义的工厂类名称,
// 将这些值作为自动配置类导入到容器中,自动配置类就生效了
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
// 3.1 //去除重复的配置类,若我们自己写的starter 可能存在重复的
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
// 4. 如果项目中某些自动配置类,我们不希望其自动配置,我们可以通过EnableAutoConfiguration的exclude或excludeName属性进行配置,
// 或者也可以在配置文件里通过配置项“spring.autoconfigure.exclude”进行配置。
//找到不希望自动配置的配置类(根据EnableAutoConfiguration注解的一个exclusions属性)
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
// 4.1 校验排除类(exclusions指定的类必须是自动配置类,否则抛出异常)
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
// 4.2 从 configurations 中,移除所有不希望自动配置的配置类
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
// 5. 对所有候选的自动配置类进行筛选,根据项目pom.xml文件中加入的依赖文件筛选出最终符合当前项目运行环境对应的自动配置类
//@ConditionalOnClass : 某个class位于类路径上,才会实例化这个Bean。
//@ConditionalOnMissingClass : classpath中不存在该类时起效
//@ConditionalOnBean : DI容器中存在该类型Bean时起效
//@ConditionalOnMissingBean : DI容器中不存在该类型Bean时起效
//@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate : DI容器中该类型Bean只有一个或@Primary的只有一个时起效
//@ConditionalOnExpression : SpEL表达式结果为true时
//@ConditionalOnProperty : 参数设置或者值一致时起效
//@ConditionalOnResource : 指定的文件存在时起效
//@ConditionalOnJndi : 指定的JNDI存在时起效
//@ConditionalOnJava : 指定的Java版本存在时起效
//@ConditionalOnWebApplication : Web应用环境下起效
//@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication : 非Web应用环境下起效
//总结一下判断是否要加载某个类的两种方式:
//根据spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties进行判断。
//要判断@Conditional是否满足
// 如@ConditionalOnClass({ SqlSessionFactory.class, SqlSessionFactoryBean.class })表示需要在类路径中存在SqlSessionFactory.class、SqlSessionFactoryBean.class这两个类才能完成自动注册。
configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
// 6. 将自动配置导入事件通知监听器
//当AutoConfigurationImportSelector过滤完成后会自动加载类路径下Jar包中META-INF/spring.factories文件中 AutoConfigurationImportListener的实现类,
// 并触发fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents事件。
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
// 7. 创建 AutoConfigurationEntry 对象
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
getCandidateConfigurations 加载自动配置类
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
// 让SpringFactoryLoader去加载一些组件的名字
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader());
// 断言,非空
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you " + "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
// 从缓存中获取
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
try {
// public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
// 加载spring.factories中的配置类信息为Enumeration
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ?
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
// 获取每一个class的类路径
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
for (String factoryImplementationName : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue())) {
// 将类路径名添加到结果集中
result.add(factoryTypeName, factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
// 添加到缓存
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
spring.factories 自动配置类的全路径名称
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitHealthIndicatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.audit.AuditAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.audit.AuditEventsEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.beans.BeansEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.cache.CachesEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraHealthIndicatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraReactiveHealthIndicatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.cloudfoundry.servlet.CloudFoundryActuatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.cloudfoundry.reactive.ReactiveCloudFoundryActuatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionsReportEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.context.properties.ConfigurationPropertiesReportEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.context.ShutdownEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseHealthIndicatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveHealthIndicatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.ElasticSearchClientHealthIndicatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.ElasticSearchJestHealthIndicatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.ElasticSearchRestHealthIndicatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.endpoint.EndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.endpoint.jmx.JmxEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.endpoint.web.WebEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.env.EnvironmentEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.health.HealthEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.health.HealthIndicatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.influx.InfluxDbHealthIndicatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.info.InfoContributorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.info.InfoEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationGraphEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceHealthIndicatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.jms.JmsHealthIndicatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.jolokia.JolokiaEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapHealthIndicatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.logging.LogFileWebEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.logging.LoggersEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.mail.MailHealthIndicatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.management.HeapDumpWebEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.management.ThreadDumpEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.CompositeMeterRegistryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.JvmMetricsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.KafkaMetricsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.Log4J2MetricsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.LogbackMetricsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.MetricsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.MetricsEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.SystemMetricsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.amqp.RabbitMetricsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.cache.CacheMetricsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.export.appoptics.AppOpticsMetricsExportAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.export.atlas.AtlasMetricsExportAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.export.datadog.DatadogMetricsExportAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.export.dynatrace.DynatraceMetricsExportAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.export.elastic.ElasticMetricsExportAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.export.ganglia.GangliaMetricsExportAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.export.graphite.GraphiteMetricsExportAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.export.humio.HumioMetricsExportAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.export.influx.InfluxMetricsExportAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.export.jmx.JmxMetricsExportAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.export.kairos.KairosMetricsExportAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.export.newrelic.NewRelicMetricsExportAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.export.prometheus.PrometheusMetricsExportAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.export.signalfx.SignalFxMetricsExportAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.export.simple.SimpleMetricsExportAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.export.statsd.StatsdMetricsExportAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.export.wavefront.WavefrontMetricsExportAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.jdbc.DataSourcePoolMetricsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.jersey.JerseyServerMetricsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.orm.jpa.HibernateMetricsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.web.client.HttpClientMetricsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.web.jetty.JettyMetricsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.web.reactive.WebFluxMetricsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.web.servlet.WebMvcMetricsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.web.tomcat.TomcatMetricsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoHealthIndicatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoReactiveHealthIndicatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.neo4j.Neo4jHealthIndicatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.redis.RedisHealthIndicatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.redis.RedisReactiveHealthIndicatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.scheduling.ScheduledTasksEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveManagementWebSecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.security.servlet.ManagementWebSecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.session.SessionsEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.solr.SolrHealthIndicatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.system.DiskSpaceHealthIndicatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.trace.http.HttpTraceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.trace.http.HttpTraceEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.web.mappings.MappingsEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveManagementContextAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.web.server.ManagementContextAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletManagementContextAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.web.ManagementContextConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.endpoint.web.ServletEndpointManagementContextConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.endpoint.web.reactive.WebFluxEndpointManagementContextConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.endpoint.web.servlet.WebMvcEndpointManagementContextConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.endpoint.web.jersey.JerseyWebEndpointManagementContextConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.web.jersey.JerseyManagementChildContextConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveManagementChildContextConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletManagementChildContextConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcEndpointChildContextConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer=\
org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.MissingRequiredConfigurationFailureAnalyzer
getExclusions去除自定义的不想自动配置的类
protected Set<String> getExclusions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
Set<String> excluded = new LinkedHashSet<>();
// 注解上的 exclude 属性
excluded.addAll(asList(attributes, "exclude"));
// 注解上的 excludeName 属性
excluded.addAll(Arrays.asList(attributes.getStringArray("excludeName")));
// 配置文件的 spring.autoconfigure.exclude 属性
excluded.addAll(getExcludeAutoConfigurationsProperty());
return excluded;
}
checkExcludedClasses校验排除类
private void checkExcludedClasses(List<String> configurations, Set<String> exclusions) {
// 获得 exclusions 不在 invalidExcludes 的集合,添加到 invalidExcludes 中
List<String> invalidExcludes = new ArrayList<>(exclusions.size());
for (String exclusion : exclusions) {
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(exclusion, getClass().getClassLoader()) // classpath 存在该类
&& !configurations.contains(exclusion)) { // configurations 不存在该类
invalidExcludes.add(exclusion);
}
}
// 如果 invalidExcludes 非空,抛出 IllegalStateException 异常
if (!invalidExcludes.isEmpty()) {
handleInvalidExcludes(invalidExcludes);
}
}
筛选filter
private List<String> filter(List<String> configurations, AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata) {
// 声明需要用到的变量
long startTime = System.nanoTime(); // 记录开始时间,用于下面统计消耗的时间
String[] candidates = StringUtils.toStringArray(configurations); // 配置类的数组
boolean[] skip = new boolean[candidates.length]; // 每个配置类是否需要忽略的数组,通过下标互相索引
boolean skipped = false; // 是否有需要忽略的
// 遍历 AutoConfigurationImportFilter 数组,逐个匹配
for (AutoConfigurationImportFilter filter : getAutoConfigurationImportFilters()) {
// 设置 AutoConfigurationImportFilter 的属性们
invokeAwareMethods(filter);
// 执行批量匹配,并返回匹配结果
boolean[] match = filter.match(candidates, autoConfigurationMetadata);
// 遍历匹配结果,判断哪些需要忽略
for (int i = 0; i < match.length; i++) {
if (!match[i]) { // 如果有不匹配的
skip[i] = true;
candidates[i] = null; // 标记为空,循环的下一次,就无需匹配它了。
skipped = true; // 标记存在不匹配的
}
}
}
// 如果没有需要忽略的,直接返回 configurations 即可
if (!skipped) {
return configurations;
}
// 如果存在需要忽略的,构建新的数组,排除掉忽略的
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>(candidates.length);
for (int i = 0; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (!skip[i]) {
result.add(candidates[i]);
}
}
// 打印,消耗的时间,已经排除的数量
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
int numberFiltered = configurations.size() - result.size();
logger.trace("Filtered " + numberFiltered + " auto configuration class in "
+ TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(System.nanoTime() - startTime)
+ " ms");
}
// 返回
return new ArrayList<>(result);
}
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents将自动配置导入事件通知监听器
private void fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(List<String> configurations, Set<String> exclusions) {
// 加载指定类型 AutoConfigurationImportListener 对应的,在 `META-INF/spring.factories` 里的类名的数组。
List<AutoConfigurationImportListener> listeners = getAutoConfigurationImportListeners();
if (!listeners.isEmpty()) {
// 创建 AutoConfigurationImportEvent 事件
AutoConfigurationImportEvent event = new AutoConfigurationImportEvent(this, configurations, exclusions);
// 遍历 AutoConfigurationImportListener 监听器们,逐个通知
for (AutoConfigurationImportListener listener : listeners) {
// 设置 AutoConfigurationImportListener 的属性
invokeAwareMethods(listener);
// 给AutoConfigurationImportListener监听器发送事件
listener.onAutoConfigurationImportEvent(event);
}
}
}
因此 springboot自动配置的流程:
- springboot应用启动;
- @SpringBootApplication起作用;
- @EnableAutoConfiguration;
- @AutoConfigurationPackage:这个组合注解主要是@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class),它通过将Registrar类导入到容器中,而Registrar类作用是扫描主配置类同级目录以及子包,并将组件AutoConfigurationPackages导入到springboot创建管理的容器中;
- @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class):它通过将AutoConfigurationImportSelector类导入到容器中,AutoConfigurationImportSelector类作用是通过selectImports方法执行的过程中,会使用内部工具类SpringFactoriesLoader,查找classpath上所有jar包中的META-INF/spring.factories进行加载,实现将配置类信息交给SpringFactory加载器进行一系列的容器创建过程
2.3 @ComponentScan 包扫描器
具体扫描的包的根路径由Spring Boot项目主程序启动类所在包位置决定,在扫描过程中由@AutoConfigurationPackage注解进行解析,从而得到Spring Boot项目主程序启动类所在包的具体位置
3 执行原理
public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(SpringbootdemoApplication.class, args);}
3.1 SpringApplication.run()
/**
* 运行 Spring 应用
*
* Static helper that can be used to run a {@link SpringApplication} from the
* specified source using default settings.
* @param primarySource the primary source to load 加载的主类
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return the running {@link ApplicationContext}
*
*/
//调用静态类,参数对应的就是SpringbootDemoApplication.class以及main方法中的args
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
/**
* 运行 Spring 应用
*
* Static helper that can be used to run a {@link SpringApplication} from the
* specified sources using default settings and user supplied arguments.
* @param primarySources the primary sources to load 加载的主类的数组
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return the running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
//SpringApplication的启动由两部分组成:
//1. 实例化SpringApplication对象
//2. run(args):调用run方法
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
3.2 SpringApplication初始化 new SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources)
/**
* Create a new {@link SpringApplication} instance. The application context will load
* beans from the specified primary sources (see {@link SpringApplication class-level}
* documentation for details. The instance can be customized before calling
* {@link #run(String...)}.
* @param primarySources the primary bean sources
* @see #run(Class, String[])
* @see #SpringApplication(ResourceLoader, Class...)
* @see #setSources(Set)
*/
public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
this(null, primarySources);
}
/**
* Create a new {@link SpringApplication} instance. The application context will load
* beans from the specified primary sources (see {@link SpringApplication class-level}
* documentation for details. The instance can be customized before calling
* {@link #run(String...)}.
* @param resourceLoader the resource loader to use
* @param primarySources the primary bean sources
* @see #run(Class, String[])
* @see #setSources(Set)
*/
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.sources = new LinkedHashSet();
this.bannerMode = Mode.CONSOLE;
this.logStartupInfo = true;
this.addCommandLineProperties = true;
this.addConversionService = true;
this.headless = true;
this.registerShutdownHook = true;
this.additionalProfiles = new HashSet();
this.isCustomEnvironment = false;
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
//项目启动类 SpringbootDemoApplication.class设置为属性存储起来
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
//设置应用类型是SERVLET应用(Spring 5之前的传统MVC应用)还是REACTIVE应用(Spring 5开始出现的WebFlux交互式应用)
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
// 设置初始化器(Initializer),最后会调用这些初始化器
//所谓的初始化器就是org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer的实现类,在Spring上下文被刷新之前进行初始化的操作
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// 设置监听器(Listener)
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
// 初始化 mainApplicationClass 属性:用于推断并设置项目main()方法启动的主程序启动类
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
3.2.1 判断应用类型 WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath()
/**
* @return 从 classpath 上,判断 Web 应用类型。
*/
static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {
// WebApplicationType.REACTIVE 类型 通过类加载器判断REACTIVE相关的Class是否存在
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) // 判断REACTIVE相关的Class是否存在
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
// WebApplicationType.NONE 类型
for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) { // 不存在 Servlet 的类
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
// WebApplicationType.SERVLET 类型。可以这样的判断的原因是,引入 Spring MVC 时,是内嵌的 Web 应用,会引入 Servlet 类。
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
3.2.2 WebApplicationType
public enum WebApplicationType {
/**
* The application should not run as a web application and should not start an
* embedded web server.
*
* 非内嵌的 Web 应用
*/
NONE,
/**
* The application should run as a servlet-based web application and should start an
* embedded servlet web server.
*
* 内嵌的 Servlet Web 应用。例如说,Spring MVC 。
*/
SERVLET,
/**
* The application should run as a reactive web application and should start an
* embedded reactive web server.
*
* 内嵌的 Reactive Web 应用。例如说,Spring Webflux 。
*/
REACTIVE;
private static final String[] SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES = { "javax.servlet.Servlet",
"org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" };
private static final String WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework."
+ "web.servlet.DispatcherServlet";
private static final String WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org."
+ "springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler";
private static final String JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer";
private static final String SERVLET_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext";
private static final String REACTIVE_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.ReactiveWebApplicationContext";
/**
* @return 从 classpath 上,判断 Web 应用类型。
*/
static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {
// WebApplicationType.REACTIVE 类型 通过类加载器判断REACTIVE相关的Class是否存在
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) // 判断REACTIVE相关的Class是否存在
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
// WebApplicationType.NONE 类型
for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) { // 不存在 Servlet 的类
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
// WebApplicationType.SERVLET 类型。可以这样的判断的原因是,引入 Spring MVC 时,是内嵌的 Web 应用,会引入 Servlet 类。
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
static WebApplicationType deduceFromApplicationContext(
Class<?> applicationContextClass) {
if (isAssignable(SERVLET_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_CLASS, applicationContextClass)) {
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
if (isAssignable(REACTIVE_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_CLASS, applicationContextClass)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
private static boolean isAssignable(String target, Class<?> type) {
try {
return ClassUtils.resolveClassName(target, null).isAssignableFrom(type);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
return false;
}
}
}
3.2.3 设置初始化器setInitializers
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class)); 设置初始化器重要的是getSpringFactoriesInstances 通过类型获取对应的初始化类
/**
* 获得指定类对应的对象。
*
* @param type 指定类
* @param <T> 泛型
* @return 对象们
* // // 这里的入参type是:org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer.class
r
* // ApplicationListener
*/
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {});
}
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
// 加载指定类型对应的,在 `META-INF/spring.factories` 里的类名的数组
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
//org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer,\
//org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging.ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener
// 根据names来进行实例化
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
// 对实例进行排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
3.2.4 创建实例 createSpringFactoriesInstances
上一步的获取类对象中有一步创建实例
/**
* 创建对象的数组
*
* @param type 父类
* @param parameterTypes 构造方法的参数类型
* @param classLoader 类加载器
* @param args 参数
* @param names 类名的数组
* @param <T> 泛型
* @return 对象的数组
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
// parameterTypes: 上一步得到的names集合
private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes, ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args,
Set<String> names) {
List<T> instances = new ArrayList<>(names.size()); // 数组大小,细节~
// 遍历 names 数组
for (String name : names) {
try {
// 获得 name 对应的类
Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);
// 确认被加载类是ApplicationContextInitializer的子类
Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
// 获得构造方法
Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass.getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes);
// 通过反射创建对象
T instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args);
//加入实例列表中
instances.add(instance);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
}
}
return instances;
}
3.2.5 设置监听器setListeners
原理同设置初始化器一样,不同的是通过类型获取实例
3.2.6 设置主程序类 deduceMainApplicationClass
private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() {
try {
// 获得当前 StackTraceElement 数组
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = new RuntimeException().getStackTrace();
// 判断哪个执行了 main 方法
for (StackTraceElement stackTraceElement : stackTrace) {
if ("main".equals(stackTraceElement.getMethodName())) {
return Class.forName(stackTraceElement.getClassName());
}
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// Swallow and continue
}
return null;
}
3.3 run() ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args)
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 创建 StopWatch 对象,并启动。StopWatch 主要用于简单统计 run 启动过程的时长。
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
// 初始化应用上下文和异常报告集合
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
// 配置 headless 属性
configureHeadlessProperty();
// (1)获取并启动监听器
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
// 创建 ApplicationArguments 对象 初始化默认应用参数类
// args是启动Spring应用的命令行参数,该参数可以在Spring应用中被访问。如:--server.port=9000
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
//(2)项目运行环境Environment的预配置
// 创建并配置当前SpringBoot应用将要使用的Environment
// 并遍历调用所有的SpringApplicationRunListener的environmentPrepared()方法
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 准备Banner打印器 - 就是启动Spring Boot的时候打印在console上的ASCII艺术字体
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// (3)创建Spring容器
context = createApplicationContext();
// 获得异常报告器 SpringBootExceptionReporter 数组
//这一步的逻辑和实例化初始化器和监听器的一样,
// 都是通过调用 getSpringFactoriesInstances 方法来获取配置的异常类名称并实例化所有的异常处理类。
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
// (4)Spring容器前置处理
//这一步主要是在容器刷新之前的准备动作。包含一个非常关键的操作:将启动类注入容器,为后续开启自动化配置奠定基础。
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
// (5):刷新容器
refreshContext(context);
// (6):Spring容器后置处理
//扩展接口,设计模式中的模板方法,默认为空实现。
// 如果有自定义需求,可以重写该方法。比如打印一些启动结束log,或者一些其它后置处理
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
// 停止 StopWatch 统计时长
stopWatch.stop();
// 打印 Spring Boot 启动的时长日志。
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
// (7)发出结束执行的事件通知
// 执行所有listener的started方法
listeners.started(context);
// (8):执行Runners
//用于调用项目中自定义的执行器XxxRunner类,使得在项目启动完成后立即执行一些特定程序
//Runner 运行器用于在服务启动时进行一些业务初始化操作,这些操作只在服务启动后执行一次。
//Spring Boot提供了ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner两种服务接口
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 如果发生异常,则进行处理,并抛出 IllegalStateException 异常
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
// (9)发布应用上下文就绪事件
//表示在前面一切初始化启动都没有问题的情况下,使用运行监听器SpringApplicationRunListener持续运行配置好的应用上下文ApplicationContext,
// 这样整个Spring Boot项目就正式启动完成了。
try {
listeners.running(context);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 如果发生异常,则进行处理,并抛出 IllegalStateException 异常
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
//返回容器
return context;
}
3.3.1 getRunListeners获取监听器并调用listeners.starting();启动
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[] { SpringApplication.class, String[].class };
// 这里仍然利用了getSpringFactoriesInstances方法来获取实例,
// 从META-INF/spring.factories中读取Key为org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener的Values
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger, getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args));
}
3.3.2 prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments); 创建并配置当前SpringBoot应用将要使用的Environment
/*
加载外部化配置资源到environment,包括命令行参数、servletConfigInitParams、
servletContextInitParams、systemProperties、sytemEnvironment、random、
application.yml(.yaml/.xml/.properties)等;初始化日志系统。
*/
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
//获取或创建环境(存在就直接返回,不存在创建一个再返回)
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
//配置环境:配置PropertySources和active Profiles
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
//listeners环境准备(就是广播ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件)。
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
//将环境绑定到SpringApplication
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
//如果非web环境,将环境转换成StandardEnvironment
// private boolean isCustomEnvironment = false;
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
// 配置PropertySources对它自己的递归依赖
// 如果有 attach 到 environment 上的 MutablePropertySources ,则添加到 environment 的 PropertySource 中。
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
- 3.3.2.1 getOrCreateEnvironment(); 获取或创建环境
/**
* @return 获得或创建 ConfigurableEnvironment 对象
*/
private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment() {
// 已经存在,则进行返回
if (this.environment != null) {
return this.environment;
}
// 不存在,则根据 webApplicationType 类型,进行创建。
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
return new StandardServletEnvironment();
case REACTIVE:
return new StandardReactiveWebEnvironment();
default:
return new StandardEnvironment();
}
}
- 3.3.2.2 configureEnvironment 配置PropertySources和active Profiles
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
// 设置 environment 的 conversionService 属性
// /**
// * 是否添加共享的 ConversionService
// */
// private boolean addConversionService = true;
if (this.addConversionService) {
ConversionService conversionService = ApplicationConversionService.getSharedInstance();
environment.setConversionService((ConfigurableConversionService) conversionService);
}
// 增加 environment 的 PropertySource 属性源
configurePropertySources(environment, args);
// 配置 environment 的 activeProfiles 属性
configureProfiles(environment, args);
}
- 3.3.2.3 configurePropertySources 增加 environment 的 PropertySource 属性源
protected void configurePropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
MutablePropertySources sources = environment.getPropertySources();
// 配置的 defaultProperties
if (this.defaultProperties != null && !this.defaultProperties.isEmpty()) {
sources.addLast(new MapPropertySource("defaultProperties", this.defaultProperties));
}
// 来自启动参数的
if (this.addCommandLineProperties && args.length > 0) {
String name = CommandLinePropertySource.COMMAND_LINE_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME;
if (sources.contains(name)) { // 已存在,就进行替换
PropertySource<?> source = sources.get(name);
CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(name);
composite.addPropertySource(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(
"springApplicationCommandLineArgs", args));
composite.addPropertySource(source);
sources.replace(name, composite);
} else { // 不存在,就进行添加
sources.addFirst(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(args));
}
}
}
- 3.3.2.4 configureProfiles 配置 environment 的 activeProfiles 属性
protected void configureProfiles(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
environment.getActiveProfiles(); // ensure they are initialized 保证已经被初始化
// But these ones should go first (last wins in a property key clash)
// /**
// * 附加的 profiles 的数组
// */
// private Set<String> additionalProfiles = new HashSet<>();
Set<String> profiles = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.additionalProfiles);
profiles.addAll(Arrays.asList(environment.getActiveProfiles()));
// 设置 activeProfiles
environment.setActiveProfiles(StringUtils.toStringArray(profiles));
}
3.3.3 createApplicationContext(); 创建Spring容器
/**
* Strategy method used to create the {@link ApplicationContext}. By default this
* method will respect any explicitly set application context or application context
* class before falling back to a suitable default.
* @return the application context (not yet refreshed)
* @see #setApplicationContextClass(Class)
*/
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
// 根据 webApplicationType 类型,获得 ApplicationContext 类型
// 这里创建容器的类型 还是根据webApplicationType进行判断的,
// 该类型为SERVLET类型,所以会通过反射装载对应的字节码,
// 也就是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
// 先判断有没有指定的实现类
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
// public static final String DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.boot."
// + "web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext";
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable create a default ApplicationContext, " + "please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex);
}
}
// 创建 ApplicationContext 对象
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
3.3.4 getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);异常报告器
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
// 加载指定类型对应的,在 `META-INF/spring.factories` 里的类名的数组
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
//org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer,\
//org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging.ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener
// 根据names来进行实例化
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
// 对实例进行排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
3.3.5 prepareContext Spring容器前置处理,将启动类注入容器,为后续开启自动化配置奠定基础
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
//设置容器环境,包括各种变量
context.setEnvironment(environment);
//设置上下文的 bean 生成器和资源加载器
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
//执行容器中的ApplicationContextInitializer(包括 spring.factories和自定义的实例)
applyInitializers(context);
//触发所有 SpringApplicationRunListener 监听器的 contextPrepared 事件方法
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
//记录启动日志
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
//注册启动参数bean,这里将容器指定的参数封装成bean,注入容器
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory).setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
// Load the sources
// 加载所有资源
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
//加载我们的启动类,将启动类注入容器,为后续开启自动化配置奠定基础
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
//触发所有 SpringApplicationRunListener 监听器的 contextLoaded 事件方法
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
//这块会对整个上下文进行一个预处理,比如触发监听器的响应事件、加载资源、设置上下文环境等等
}
- 3.3.5.1 applyInitializers(context); 执行容器中的ApplicationContextInitializer
/*
用到了在创建SpringApplication实例时设置的初始化器了,依次对它们进行遍历,并调用initialize方法。
我们也可以自定义初始化器,并实现initialize方法,然后放入META-INF/spring.factories配置文件中
Key为:org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer的value中,
这里我们自定义的初始化器就会被调用,是我们项目初始化的一种方式
*/
protected void applyInitializers(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
// 1. 从SpringApplication类中的initializers集合获取所有的ApplicationContextInitializer
for (ApplicationContextInitializer initializer : getInitializers()) {
// 2. 循环调用ApplicationContextInitializer中的initialize方法
// 校验 ApplicationContextInitializer 的泛型非空
Class<?> requiredType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(initializer.getClass(), ApplicationContextInitializer.class);
Assert.isInstanceOf(requiredType, context, "Unable to call initializer.");
// 初始化 ApplicationContextInitializer
initializer.initialize(context);
}
}
- 3.3.5.2 load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0])); 加载启动类 注册bean
/**
* Load beans into the application context.
* @param context the context to load beans into
* @param sources the sources to load
*/
protected void load(ApplicationContext context, Object[] sources) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loading source " + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(sources));
}
// 创建 BeanDefinitionLoader 对象
BeanDefinitionLoader loader = createBeanDefinitionLoader(getBeanDefinitionRegistry(context), sources);
// 设置 loader 的属性
if (this.beanNameGenerator != null) {
loader.setBeanNameGenerator(this.beanNameGenerator);
}
if (this.resourceLoader != null) {
loader.setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
}
if (this.environment != null) {
loader.setEnvironment(this.environment);
}
// 执行 BeanDefinition 加载
loader.load();
}
/**
* Load the sources into the reader.
* @return the number of loaded beans
*/
public int load() {
int count = 0;
// 遍历 sources 数组,逐个加载
for (Object source : this.sources) {
count += load(source);
}
return count;
}
private int load(Object source) {
Assert.notNull(source, "Source must not be null");
// 如果是 Class 类型,则使用 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 执行加载
if (source instanceof Class<?>) {
return load((Class<?>) source);
}
// 如果是 Resource 类型,则使用 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 执行加载
if (source instanceof Resource) {
return load((Resource) source);
}
// 如果是 Package 类型,则使用 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 执行加载
if (source instanceof Package) {
return load((Package) source);
}
// 如果是 CharSequence 类型,则各种尝试去加载
if (source instanceof CharSequence) {
return load((CharSequence) source);
}
// 无法处理的类型,抛出 IllegalArgumentException 异常
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid source type " + source.getClass());
}
- 3.3.5.3 load() 多个load方法
private int load(Class<?> source) {
// Groovy 相关,暂时忽略
if (isGroovyPresent()
&& GroovyBeanDefinitionSource.class.isAssignableFrom(source)) {
// Any GroovyLoaders added in beans{} DSL can contribute beans here
GroovyBeanDefinitionSource loader = BeanUtils.instantiateClass(source, GroovyBeanDefinitionSource.class);
load(loader);
}
// 如果是 Component ,则执行注册
if (isComponent(source)) {
this.annotatedReader.register(source);
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// Groovy 相关,暂时忽略
private int load(GroovyBeanDefinitionSource source) {
int before = this.xmlReader.getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
((GroovyBeanDefinitionReader) this.groovyReader).beans(source.getBeans());
int after = this.xmlReader.getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
return after - before;
}
private int load(Resource source) {
// Groovy 相关,暂时忽略
if (source.getFilename().endsWith(".groovy")) {
if (this.groovyReader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Cannot load Groovy beans without Groovy on classpath");
}
return this.groovyReader.loadBeanDefinitions(source);
}
// 使用 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 加载 BeanDefinition
return this.xmlReader.loadBeanDefinitions(source);
}
private int load(Package source) {
return this.scanner.scan(source.getName());
}
private int load(CharSequence source) {
// 解析 source 。因为,有可能里面带有占位符。
String resolvedSource = this.xmlReader.getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(source.toString());
// 尝试按照 Class 进行加载
// Attempt as a Class
try {
return load(ClassUtils.forName(resolvedSource, null));
} catch (IllegalArgumentException | ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// swallow exception and continue
}
// 尝试按照 Resource 进行加载
// Attempt as resources
Resource[] resources = findResources(resolvedSource);
int loadCount = 0;
boolean atLeastOneResourceExists = false;
for (Resource resource : resources) {
if (isLoadCandidate(resource)) {
atLeastOneResourceExists = true;
loadCount += load(resource);
}
}
if (atLeastOneResourceExists) { // 有加载到,则认为成功,返回。
return loadCount;
}
// Attempt as package
// 尝试按照 Package 进行加载
Package packageResource = findPackage(resolvedSource);
if (packageResource != null) {
return load(packageResource);
}
// 无法处理,抛出 IllegalArgumentException 异常
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid source '" + resolvedSource + "'");
}
private boolean isGroovyPresent() {
return ClassUtils.isPresent("groovy.lang.MetaClass", null);
}
private Resource[] findResources(String source) {
// 创建 ResourceLoader 对象
ResourceLoader loader = (this.resourceLoader != null) ? this.resourceLoader : new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
try {
// 获得 Resource 数组
if (loader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
return ((ResourcePatternResolver) loader).getResources(source);
}
// 获得 Resource 对象
return new Resource[] { loader.getResource(source) };
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Error reading source '" + source + "'");
}
}
private boolean isLoadCandidate(Resource resource) {
// 不存在,则返回 false
if (resource == null || !resource.exists()) {
return false;
}
// 判断 resource 是 ClassPathResource 类,不是一个 package
if (resource instanceof ClassPathResource) {
// A simple package without a '.' may accidentally get loaded as an XML
// document if we're not careful. The result of getInputStream() will be
// a file list of the package content. We double check here that it's not
// actually a package.
String path = ((ClassPathResource) resource).getPath();
if (path.indexOf('.') == -1) {
try {
return Package.getPackage(path) == null;
} catch (Exception ex) {
// Ignore
}
}
}
// 返回 true ,符合条件
return true;
}
private Package findPackage(CharSequence source) {
// 获得 source 对应的 Package 。如果存在,则返回
Package pkg = Package.getPackage(source.toString());
if (pkg != null) {
return pkg;
}
try {
// Attempt to find a class in this package
// 创建 ResourcePatternResolver 对象
ResourcePatternResolver resolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(getClass().getClassLoader());
// 尝试加载 source 目录下的 class 们
Resource[] resources = resolver.getResources(ClassUtils.convertClassNameToResourcePath(source.toString()) + "/*.class");
// 遍历 resources 数组
for (Resource resource : resources) {
// 获得类名
String className = StringUtils.stripFilenameExtension(resource.getFilename());
// 按照 Class 进行加载 BeanDefinition
load(Class.forName(source.toString() + "." + className));
break;
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
// swallow exception and continue
}
// 返回 Package
return Package.getPackage(source.toString());
}
private boolean isComponent(Class<?> type) {
// This has to be a bit of a guess. The only way to be sure that this type is
// eligible is to make a bean definition out of it and try to instantiate it.
// 如果有 @Component 注解,则返回 true
if (AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(type, Component.class) != null) {
return true;
}
// Nested anonymous classes are not eligible for registration, nor are groovy
// closures
// 暂时忽略
if (type.getName().matches(".*\\$_.*closure.*") || type.isAnonymousClass()
|| type.getConstructors() == null || type.getConstructors().length == 0) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
3.3.6 refreshContext(context); 刷新容器
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#refreshContext
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
// 开启(刷新)Spring 容器,通过refresh方法对整个IoC容器的初始化(包括Bean资源的定位、解析、注册等等)
refresh(context);
// 注册 ShutdownHook 钩子
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
try {
//向JVM运行时注册一个关机钩子,在JVM关机时关闭这个上下文,除非它当时已经关闭
context.registerShutdownHook();
} catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments.
}
}
}
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#refresh
/**
* Refresh the underlying {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param applicationContext the application context to refresh
*/
protected void refresh(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
// 断言,判断 applicationContext 是 AbstractApplicationContext 的子类
Assert.isInstanceOf(AbstractApplicationContext.class, applicationContext);
// 启动(刷新) AbstractApplicationContext
((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh();
}
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh 执行Spring容器的刷新方法,在这个方法中会初始化Tomcat容器
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
this.prepareRefresh();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory();
this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
this.initMessageSource();
this.initApplicationEventMulticaster();
this.onRefresh();
this.registerListeners();
this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
this.finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException var9) {
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var9);
}
this.destroyBeans();
this.cancelRefresh(var9);
throw var9;
} finally {
this.resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
- 3.3.6.1 初始化Tomcat onRefresh()
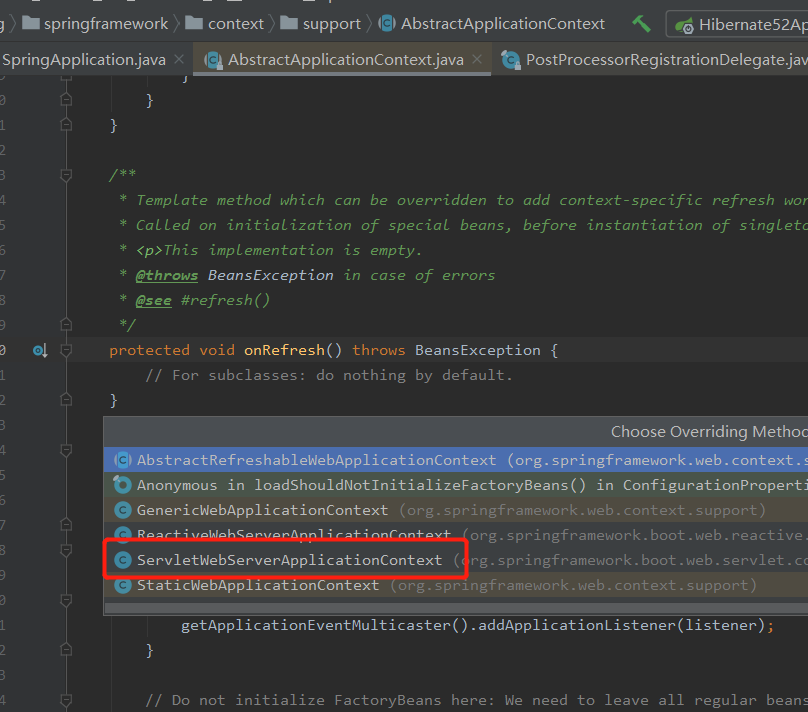
org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext#onRefresh
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
// 调用父方法
super.onRefresh();
try {
// 创建 WebServer
createWebServer();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext#createWebServer
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
// 如果 webServer 为空,说明未初始化
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
// 获得 ServletWebServerFactory 对象
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
// 获得 ServletContextInitializer 对象
// 创建(获得) WebServer 对象
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
// TODO 芋艿这个情况是?
} else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
} catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex);
}
}
// 初始化 PropertySource
initPropertySources();
}
protected ServletWebServerFactory getWebServerFactory() {
// Use bean names so that we don't consider the hierarchy
// 获得 ServletWebServerFactory 类型对应的 Bean 的名字们
String[] beanNames = getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(ServletWebServerFactory.class);
// 如果是 0 个,抛出 ApplicationContextException 异常,因为至少要一个
if (beanNames.length == 0) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to missing " + "ServletWebServerFactory bean.");
}
// 如果是 > 1 个,抛出 ApplicationContextException 异常,因为不知道初始化哪个
if (beanNames.length > 1) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to multiple " + "ServletWebServerFactory beans : " + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(beanNames));
}
// 获得 ServletWebServerFactory 类型对应的 Bean 对象
return getBeanFactory().getBean(beanNames[0], ServletWebServerFactory.class);
}
ServletWebServerFactory的实现类: 因为当前web的类型为Servlet 所以使用的实现类就是 TomcatServletWebServerFactory
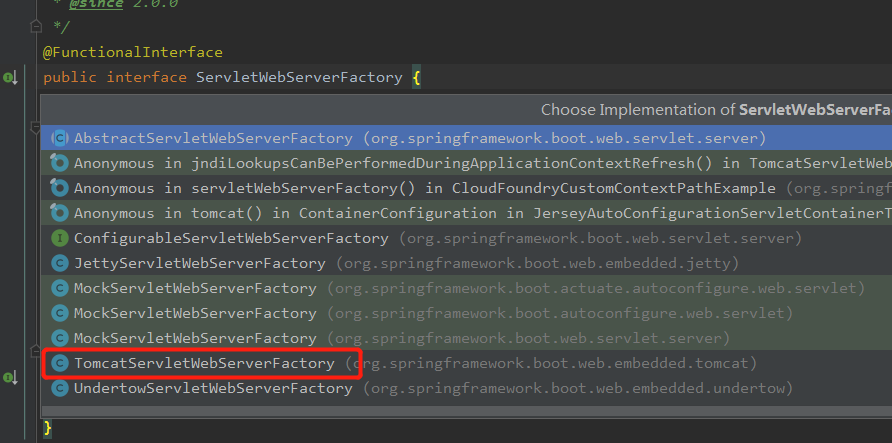
org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory#getWebServer
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
//初始化Tomcat
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
// 设置参数
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory
: createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
// 准备容器
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
// 获取容器并启动
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
protected TomcatWebServer getTomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat) {
return new TomcatWebServer(tomcat, getPort() >= 0);
}
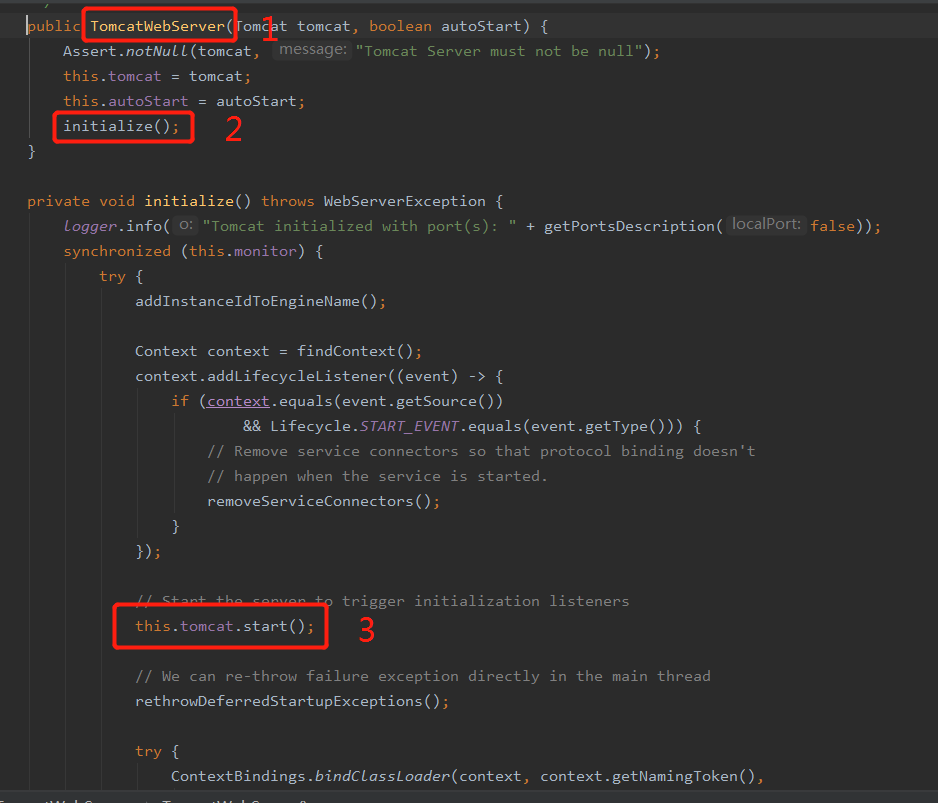
3.3.7 Spring容器后置处理 afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
protected void afterRefresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
//该方法没有实现,可以根据需要做一些定制化的操作。
}
3.3.8 执行Runners callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
自定义的执行器XxxRunner类,用于在服务启动时进行一些业务初始化操作,这些操作只在服务启动后执行一次。 Spring Boot提供了ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner两种服务接口
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
// 获得所有 Runner 们
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();
// 获得所有 ApplicationRunner 实现类
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
// 获得所有 CommandLineRunner 实现类
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
// 排序 runners
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
// 遍历 Runner 数组,执行逻辑
for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);
}
}
}
3.3.9 发布应用上下文就绪事件 listeners.running(context);
public void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
//触发所有 SpringApplicationRunListener 监听器的 running 事件方法。
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
listener.running(context);
}
}
这样整个Spring Boot项目就正式启动完成了。