Mybatis源码解析
mybatis架构原理
1. 架构设计
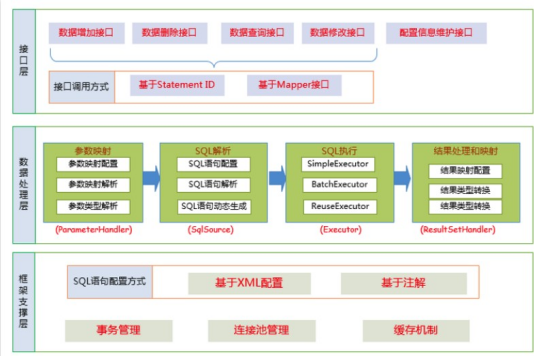 我们把Mybatis的功能架构分为三层:
我们把Mybatis的功能架构分为三层:
(1) API接口层:提供给外部使用的接口 API,开发人员通过这些本地API来操纵数据库。接口层一接收到调用请求就会调用数据处理层来完成具体的数据处理。
MyBatis和数据库的交互有两种方式:
a. 使用传统的MyBati s提供的API ;
b. 使用Mapper代理的方式
(2) 数据处理层:负责具体的SQL查找、SQL解析、SQL执行和执行结果映射处理等。它主要的目的是根据调用的请求完成一次数据库操作。
(3) 基础支撑层:负责最基础的功能支撑,包括连接管理、事务管理、配置加载和缓存处理,这些都是共 用的东西,将他们抽取出来作为最基础的组件。为上层的数据处理层提供最基础的支撑
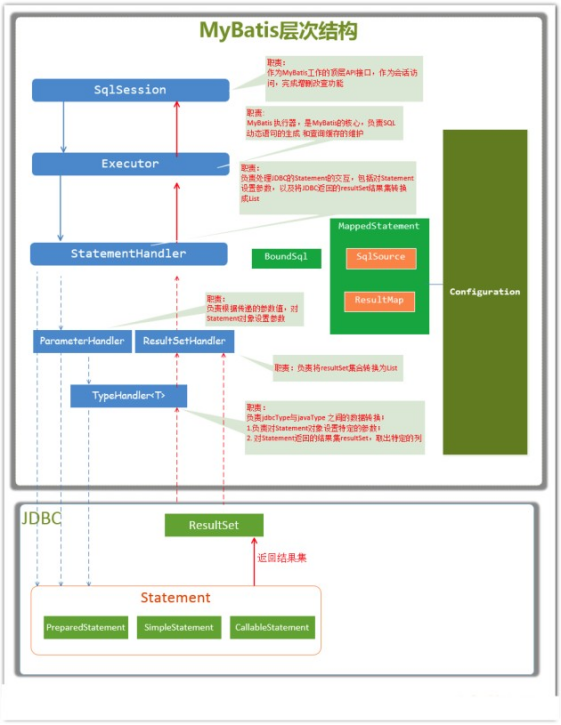
主要构件及其相互关系
| 构件 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| SqlSession | 作为MyBatis工作的主要顶层API,表示和数据库交互的会话,完成必要数 据库增删改查功能 |
| Executor | MyBatis执行器,是MyBatis调度的核心,负责SQL语句的生成和查询缓 存的维护 |
| StatementHandler | 封装了JDBC Statement操作,负责对JDBC statement的操作,如设置参数、将Statement结果集转换成List集合 |
| ParameterHandler | 负责对用户传递的参数转换成JDBC Statement所需要的参数 |
| ResultSetHandler | 负责将JDBC返回的ResultSet结果集对象转换成List类型的集合 |
| TypeHandler | 负责java数据类型和jdbc数据类型之间的映射和转换 |
| MappedStatement | MappedStatement维护了一条<select>等节点的封装 |
| SqlSource | 负责根据用户传递的parameterObject,动态地生成SQL语句,将信息封装到BoundSql对象中,并返回 |
| BoundSql | 表示动态生成的SQL语句以及相应的参数信息 |
总体流程
1. 加载配置并初始化
触发条件 加载配合文件 配置来源于两个地方,一个是配置文件(核心配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml和mapper映射文件),一个是java代码中的注解,将主配置文件内容解析封装到Configuration中,将sql的配置信息加载成一个MappedStatement并存储在内存中
2.接受调用请求
触发条件: 调用mybatis提供的api 传入参数: 为sql的ID和传入参数对象 处理过程: 将请求传递给下层的请求处理层进行处理
3.处理操作请求
触发条件: api接口层传递请求过来 传入参数:为sql的ID和传入参数对象 处理过程:
- 根据sql的ID查找对应的MappedStatement对象
- 根据传参数对象解析MappedStatement对象,的到最后要执行的sql和执行传入参数
- 获取数据库连接,根据得到的最终sql语句接执行传入UC桉树得到数据库执行,并得到执行结果
- 根据MappedStatement对象中的结果映射配置对得到的执行结果进行转换处理,并得到最后的处理结果
- 释放链接资源
4.返回处理结果
将最中的结果返回
源码剖析
传统方式源码剖析
1. 初始化
Inputstream inputstream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
//这一行代码正是初始化工作的开始。
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
使用 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build()方法构建SqlSessionFactory
// 1.我们最初调用的build
public SqlSessionFactory build (InputStream inputStream){
//调用了重载方法
return build(inputStream, null, null);
}
// 2.调用的重载方法
public SqlSessionFactory build (InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties){
try {
// XMLConfigBuilder是专门解析mybatis的配置文件的类
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputstream, environment, properties);
//这里又调用了一个重载方法。parser.parse()的返回值是Configuration对象
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e)
}
}
// 3. 调用重载方法
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
//创建了 DefaultSqlSessionFactory 对象,传入 Configuration 对象
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
Mybatis在初始化的时候,会将MyBatis的配置信息全部加载到内存中,使用org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration 实例来维护
2. 配置文件解析
- Configuration Configuration对象的结构和xml配置文件的对象几乎相同 xml中的配置标签: properties(属性)、settings(设置)、 typeAliases(别名类型)、typeHandlers(类型处理器)、ObjectFactory(对象工厂)、mappers(映射器)等 Configuration也有对应的属性来封装这些 也就是说,初始化配置文件的本质就是创建Configuration对象,讲解析的xml中的数据封装到Configuration中
/**
* 解析 XML 成 Configuration 对象。
*
* @return Configuration 对象
*/
public Configuration parse() {
// 若已解析,抛出 BuilderException 异常
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
// 标记已解析
parsed = true;
///parser是XPathParser解析器对象,读取节点内数据,<configuration>是MyBatis配置文件中的顶层标签
// 解析 XML configuration 节点
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
/**
* 解析 XML
*
* 具体 MyBatis 有哪些 XML 标签,参见 《XML 映射配置文件》http://www.mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/configuration.html
*
* @param root 根节点
*/
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//issue #117 read properties first
// 解析 <properties /> 标签
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
// 解析 <settings /> 标签
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
// 加载自定义的 VFS 实现类
loadCustomVfs(settings);
// 解析 <typeAliases /> 标签
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
// 解析 <plugins /> 标签
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
// 解析 <objectFactory /> 标签
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
// 解析 <objectWrapperFactory /> 标签
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
// 解析 <reflectorFactory /> 标签
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
// 赋值 <settings /> 到 Configuration 属性
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
// 解析 <environments /> 标签
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
// 解析 <databaseIdProvider /> 标签
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
// 解析 <typeHandlers /> 标签
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
// 解析 <mappers /> 标签
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
- MappedStatement MappedStatement与Mapper配置文件中的一个select/update/insert/delete节点相对应。 mapper中配置的标签都被封装到了此对象中,主要用途是描述一条SQL语句
初始化过程:
在Configuration解析时,会将Mapper.xml中的内容全部解析成一个MappedStatement列表,存储在Configuration中的mappedStatements属性中,mappedStatements是一个HashMap,存储时,key=全限定类名+方法名,value=对应的MappedStatement对象
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
......
省略其他内容
// 解析 <mappers /> 标签
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
在Configuration中对应的属性为: Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new StrictMap<>("Mapped Statements collection")
3. 执行sql
-
SqlSession
SqlSession是一个接口。有两个实现类: DefaultSqlSession (默认) SqlSessionManager (弃用) SqlSession是MyBatis中用于和数据库交互的顶层类,通常将它与ThreadLocal绑定,一个会话使用一 个SqlSession,并且在使用完毕后需要close
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
private final Configuration configuration;
private final Executor executor;
......
}
SqlSession中有两个重要的参数
configuration(与初始化的相同)、
executor(执行器)
Executor也是一个接口,有三个常用的实现类:
BatchExecutor (重用语句并执行批量操作)
ReuseExecutor (重用预处理语句 prepared statement)
SimpleExecutor (普通的执行器 默认)
-
执行sql 以selectList为例
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionFactory.openSession(); sqlSession.selectList("com.example.mapper.UserMapper.findById");
获取SqlSession
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
//getDefaultExecutorType()传递的是SimpleExecutor
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
//ExecutorType 为Executor的类型,TransactionIsolationLevel为事务隔离级别,autoCommit是否开启事务
//openSession的多个重载方法可以指定获得的SeqSession的Executor类型和事务的处理
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
// 获得 Environment 对象
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
// 创建 Transaction 对象
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
// 创建 Executor 对象
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
// 创建 DefaultSqlSession 对象
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 如果发生异常,则关闭 Transaction 对象
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
执行SqlSession中的Api
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement) {
return this.selectList(statement, null);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.selectList(statement, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
// 获得 MappedStatement 对象
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// 执行查询
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
4.executor
进入executor.query()
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
//根据传入的参数动态获得SQL语句,最后返回用BoundSql对象表示
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
//为本次查询创建缓存的Key
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
// 查询
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
// 从数据库中读取操作
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
// 在缓存中,添加占位对象。此处的占位符,和延迟加载有关,可见 `DeferredLoad#canLoad()` 方法
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
// 执行读操作
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
// 从缓存中,移除占位对象
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
// 添加到缓存中
localCache.putObject(key, list);
// 暂时忽略,存储过程相关
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
//doQuery方法 抽象 查找子类的实现方法
protected abstract <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException;
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 传入参数创建StatementHanlder对象来执行查询
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 创建jdbc中的statement对象
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 执行 StatementHandler ,进行读操作
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
// 关闭 StatementHandler 对象
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
// 初始化 StatementHandler 对象
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
// 获得 Connection 对象
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
// 创建 Statement 或 PrepareStatement 对象
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// 设置 SQL 上的参数,例如 PrepareStatement 对象上的占位符
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
//查看getConnection()
//BaseExecutor中的getConnection()
// 获得 Connection 对象
protected Connection getConnection(Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
// 获得 Connection 对象
Connection connection = transaction.getConnection();
// 如果 debug 日志级别,则创建 ConnectionLogger 对象,进行动态代理
if (statementLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
return ConnectionLogger.newInstance(connection, statementLog, queryStack);
} else {
return connection;
}
}
//查看transaction中以及实现类JdbcTransaction中的getConnection()
Connection getConnection() throws SQLException;
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
// 连接为空,进行创建
if (connection == null) {
openConnection();
}
return connection;
}
/**
* 获得 Connection 对象
*
* @throws SQLException 获得失败
*/
protected void openConnection() throws SQLException {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection");
}
// 获得连接
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
// 设置隔离级别
if (level != null) {
connection.setTransactionIsolation(level.getLevel());
}
// 设置 autoCommit 属性
setDesiredAutoCommit(autoCommit);
}
Executor.query()方法最后会创建一个StatementHandler对象,然后将必要的参数传递给StatementHandler,使用StatementHandler来完成对数据库的查询,最终返回List结果集
Executor的功能和作用是:
a、根据传递的参数,完成SQL语句的动态解析,生成BoundSql对象,供StatementHandler使用;
b、为查询创建缓存,以提高性能
c、创建JDBC的Statement连接对象,传递给*StatementHandler*对象,返回List查询结果。
5. StatementHandler
StatementHandler对象主要完成两个工作:
对于JDBC的PreparedStatement类型的对象,创建的过程中,我们使用的是SQL语句字符串会包含若干个?占位符,我们其后再对占位符进行设值。StatementHandler通过
parameterize(statement)方法对 Statement 进行设值;
StatementHandler 通过 List query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler)方法来完成执行Statement,和将Statement对象返回的resultSet封装成List;
进入到 StatementHandler 的实现类PreparedStatementHandler中 parameterize(statement)方法
@Override
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
//使用ParameterHandler对象来完成对Statement的设值
parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement);
}
/** ParameterHandler 类的 setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) 实现 * 对某一个Statement进行设置参数 */
@SuppressWarnings("Duplicates")
@Override
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
// 遍历 ParameterMapping 数组
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
// 获得 ParameterMapping 对象
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
// 获得值
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { // issue #448 ask first for additional params
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
// 获得 typeHandler、jdbcType 属性
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
// 设置 ? 占位符的参数
try {
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException | SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
从上述的代码可以看到,StatementHandler的parameterize(Statement)方法调用了ParameterHandler的setParameters(statement)方法, ParameterHandler的setParameters(Statement)方法负责根据我们输入的参数,对statement对象的 ?占位符处进行赋值。
进入到StatementHandler 的 List query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler)方法的实现
/**
* 执行读操作
*
* @param statement Statement 对象
* @param resultHandler ResultHandler 对象,处理结果
* @param <E> 泛型
* @return 读取的结果
*/
<E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException;
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
// 执行查询
ps.execute();
// 处理返回结果
return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps);
}
ResultSetHandler 的 handleResultSets(Statement)方法会将 Statement 语句执行后生成的 resultSet结果集转换成List结果集
/**
* 处理 {@link java.sql.ResultSet} 成映射的对应的结果
*
* @param stmt Statement 对象
* @param <E> 泛型
* @return 结果数组
*/
<E> List<E> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException;
@Override
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(mappedStatement.getId());
// 多 ResultSet 的结果集合,每个 ResultSet 对应一个 Object 对象。而实际上,每个 Object 是 List<Object> 对象。
// 在不考虑存储过程的多 ResultSet 的情况,普通的查询,实际就一个 ResultSet ,也就是说,multipleResults 最多就一个元素。
final List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList<>();
int resultSetCount = 0;
// 获得首个 ResultSet 对象,并封装成 ResultSetWrapper 对象
ResultSetWrapper rsw = getFirstResultSet(stmt);
// 获得 ResultMap 数组
// 在不考虑存储过程的多 ResultSet 的情况,普通的查询,实际就一个 ResultSet ,也就是说,resultMaps 就一个元素。
List<ResultMap> resultMaps = mappedStatement.getResultMaps();
int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size();
validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount); // 校验
while (rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) {
// 获得 ResultMap 对象
ResultMap resultMap = resultMaps.get(resultSetCount);
// 处理 ResultSet ,将结果添加到 multipleResults 中
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, null);
// 获得下一个 ResultSet 对象,并封装成 ResultSetWrapper 对象
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
// 清理
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
// resultSetCount ++
resultSetCount++;
}
// 因为 `mappedStatement.resultSets` 只在存储过程中使用,本系列暂时不考虑,忽略即可
String[] resultSets = mappedStatement.getResultSets();
if (resultSets != null) {
while (rsw != null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) {
ResultMapping parentMapping = nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]);
if (parentMapping != null) {
String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId();
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId);
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, null, parentMapping);
}
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
}
// 如果是 multipleResults 单元素,则取首元素返回
return collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults);
}
mapper代理方式
1. 写法
public class MybatisTest {
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Before
public void before() throws IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
this.userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
}
@Test
public void test2() throws IOException {
User user = this.userMapper.findById(1);
System.out.println(user);
}
}
当解析mappers标签时,它会判断解析到的是mapper配置文件时,会再将对应配置文件中的增删 改查标签 封装成MappedStatement对象,存入mappedStatements中。
当判断解析到接口时,会建此接口对应的MapperProxyFactory对象,存入HashMap中,key =接口的字节码对象,value =此接口对应的MapperProxyFactory对象。
-
getmapper()
进入sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class)方法中
/**
* Retrieves a mapper.
* @param <T> the mapper type
* @param type Mapper interface class
* @return a mapper bound to this SqlSession
*/
<T> T getMapper(Class<T> type);
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.<T>getMapper(type, this);
}
查看configuration中的getMapper()
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
查看mapperRegistry中的getMapper()
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
// 获得 MapperProxyFactory 对象
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
// 不存在,则抛出 BindingException 异常
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
/// 通过动态代理工厂生成实例。
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
查看mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession)
//MapperProxyFactory类中的newInstance方法
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
// 创建了JDK动态代理的invocationHandler接口的实现类mapperProxy
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
// 调用了重载方法
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
最后调用了Proxy.newProxyInstance() 传递了一个InvocationHandler : mapperProxy 查看mapperProxy
/**
* Mapper Proxy
*
* @author Clinton Begin
* @author Eduardo Macarron
*/
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;
/**
* SqlSession 对象
*/
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
/**
* Mapper 接口
*/
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
/**
* 方法与 MapperMethod 的映射
*
* 从 {@link MapperProxyFactory#methodCache} 传递过来
*/
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;
// 构造,传入了SqlSession,说明每个session中的代理对象的不同的!
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 如果是 Object 定义的方法,直接调用
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
// 获得 MapperMethod 对象
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
// 重点在这:MapperMethod最终调用了执行的方法
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
//省略部分代码
}
因为使用了动态代理,调用mapper类中的方法时,会先执行MapperProxy中的invoke()
查看invoke()中的execute()
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
//判断mapper中的方法类型,最终调用的还是SqlSession中的方法
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
// 转换参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 执行 INSERT 操作
// 转换 rowCount
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
// 转换参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 转换 rowCount
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
// 转换参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 转换 rowCount
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
// 无返回,并且有 ResultHandler 方法参数,则将查询的结果,提交给 ResultHandler 进行处理
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
// 执行查询,返回列表
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
// 执行查询,返回 Map
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
// 执行查询,返回 Cursor
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
// 执行查询,返回单个对象
} else {
// 转换参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 查询单条
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional() &&
(result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
// 返回结果为 null ,并且返回类型为基本类型,则抛出 BindingException 异常
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
// 返回结果
return result;
}
最终还是执行sqlSession.insert()、sqlSession.update()等方法